Usage¶
To use Material Mechanics in a project:
import material_mechanics as mm
Creating materials¶
Creating an orthotropic elastic material:
import material_mechanics as mm
name = 'Orthotropic Material'
stiffnesses = dict(e1=100000, e2=8000, e3=7000, g12=5000, g13=5000, g23=4000)
poissons = dict(nu12=0.33, nu21=0.02, nu13=0.33, nu31=0.02, nu23=0.33, nu32=0.02)
density = 1.0
material = mm.orthotropic_material(
name=name, stiffness=stiffnesses, poisson=poissons, density=density
)
Creating a transverse isotropic material:
import material_mechanics as mm
name = 'cfrp'
stiffnesses = dict(e1=140000, e2=9000, g12=4600)
poissons = dict(nu12=0.3, nu23=0.37)
strengths = None
density = 1.5
material = mm.transverse_isotropic_material(
name=name, stiffness=stiffnesses, poisson=poissons,
strength=strengths, density=density
)
Creating a fiber reinforced material:
import material_mechanics as mm
# fiber definition
name = 'Carbon Fiber HT'
stiffness = dict(e1=230000, e2=13000, g12=50000)
poisson = dict(nu12=0.23, nu23=0.3)
fiber = mm.transverse_isotropic_material(name=name, stiffness=stiffness, poisson=poisson, density=1.74)
# matrix definition
name = 'Epoxy Resin'
matrix = mm.isotropic_material(name=name, stiffness=3200.0, poisson=0.3, density=1.2)
# fiber volume content
phi = 0.65
# fiber reinfored material initialization
frp_material = mm.FiberReinforcedPlastic(
fiber_material=fiber, matrix_material=matrix, fiber_volume_fraction=phi
)
In this example we are using a factory that allows for easy laminate creation using a single material. First we create a FRP that we want to use as the material for each layer
Forst we initialize the FRP material:
import material_mechanics as mm
# fiber definition
name = 'Carbon Fiber HT'
stiffness = dict(e1=230000, e2=13000, g12=50000)
poisson = dict(nu12=0.23, nu23=0.3)
fiber = mm.transverse_isotropic_material(name=name, stiffness=stiffness, poisson=poisson, density=1.74)
# matrix definition
name = 'Epoxy Resin'
matrix = mm.isotropic_material(name=name, stiffness=3200.0, poisson=0.3, density=1.2)
# fiber volume content
phi = 0.65
# fiber reinfored material initialization
frp_material = mm.FiberReinforcedPlastic(
fiber_material=fiber, matrix_material=matrix, fiber_volume_fraction=phi
)
Now we will initialize the factory that will create the laminates:
# Laminate Factory initialization
LaminateCreator = mm.SingleMaterialLaminateFactory(frp_material)
And finally we create a laminate by providing a stacking order:
stacking_order = [(0.25, 0),(0.5, 30),(0.4, 60),(0.1, 90)]
laminate = LaminateCreator.get_laminate(stacking)
If we want a symmetric laminate, we can define the symmetry plane by the keyword ‘symmetry’ to either be at the center of the last layer (‘center_layer’) of the initial stacking or at the bottom of the last provided layer (‘full’):
# symmetric laminate with the center plane of the last layer (0.1, 90) as the laminates symmetry plane
laminate = LaminateCreator.get_laminate(stacking, symmetry='center_layer')
# symmetric laminate with the bottom plane of the last layer (0.1, 90) as the laminates symmetry plane
laminate = LaminateCreator.get_laminate(stacking, symmetry='full')
Strength analysis¶
Applying a load and calculating the puck material exertions of a laminate requires to provide the strength of the material of the layer material. in the case of fiber reinforced material five strength parameters are needed. - tensile strength in fiber direction (11_tensile) - compression strength in fiber direction (11_compression) - tensile strength prependicular to the fiber direction (22_tensile) - tensile strength in fiber direction (22_compression) - shear strength under parallel/perpendicular stress (12)
Creating the Laminate:
import material_mechanics as mm
import numpy as np
# fiber definition
name = 'Carbon Fiber HT'
stiffness = dict(e1=230000, e2=13000, g12=50000)
poisson = dict(nu12=0.23, nu23=0.3)
fiber = pm.transverse_isotropic_material(name=name, stiffness=stiffness, poisson=poisson, density=1.74)
# matrix definition including it's strength
name = 'Epoxy Resin'
matrix = pm.isotropic_material(name=name, stiffness=3200.0, poisson=0.3, density=1.2, strength=90.0)
# definition of composite material strength at target fiber volume ratio
strength_dict = dict(
r_11_tensile=2000.0, r_11_compression=1650.0,
r_22_tensile=70., r_22_compression=240.,
r_12=105,
)
# fiber reinfored material initialization
frp_material = pm.FiberReinforcedPlastic(
fiber_material=fiber(), matrix_material=matrix, fiber_volume_fraction=phi, name=None, symmetry='mean'
)
# Laminate definition
LaminateCreator = pm.SingleMaterialLaminateFactory(frp_material)
stacking_order = [(0.25, 0),(0.25, 45),(0.25, 90),(0.25, -45)]
laminate = LaminateCreator.get_laminate(stacking, symmetry='full')
Now all that is left to do is to define a load vector and to calculate the results. The load is defined as line loads
and line moments with six entries. The damage criterion used when analysing a laminate is the puck2D criterion.
The provided load vector consist of the following entries:
(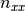 ,
, 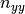 ,
, 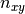 ,
, 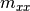 ,
, 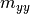 ,
, 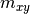 ),
where
),
where 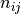 are the line loads and
are the line loads and 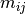 the line moments
the line moments
Strength analysis:
line_load = np.array([250, 34, 55, 4, 34, 11])
max_fb, max_zfb, laminate_exertions = puck.get_laminate_exertions(laminate=fzb_lam, line_loads=line_load)
The result is a tuple holding the maximum fiber-exertion and inter-fiber-exertion in any layer of the laminate and a list holding a dict for every layer in the laminate with detailed information about that layer, including damage indicators.